What is Capital Gains Tax? - Types, Tax Rates, Calculation, Exemptions & Tax Rates
You've just made a savvy investment in the stock market, watched your portfolio grow, and decided to cash in on your success by selling some of your stocks. But before you celebrate your financial triumph, there's one thing you can't overlook: capital gains tax.
Capital Gain Tax in India is the tax imposed by the government on the profit earned from the sale of certain assets, such as stocks, bonds, real estate, or other investments. This tax applies to both individuals and businesses.
In this guide, we have covered important aspects related to capital gains tax, capital gains tax in India, capital assets, their calculation, the Cost Inflation Index (CII), and much more in a very lucid and comprehensive manner.
What is Capital Gains?
Capital gains tax is a tax imposed on the profits realized from the sale of assets such as stocks, bonds, real estate, and other investments. It is the tax applied to the difference between an asset's purchase price (or "cost basis") and its selling price.
When you sell an asset for more than you paid for it, you have a capital gain. Conversely, if you sell an asset for less than you paid for it, you have a capital loss. Capital gains tax is typically only applied to capital gains, not to the total amount received from the sale.
To understand capital gains, you need to understand the concept of capital assets.
What are Capital Assets?
Capital assets are the property you own and can be transferred, like land, buildings, shares, patents, trademarks, jewelry, leasehold rights, machinery, vehicles, etc.
Here is a list of assets that do not fall under the category of capital assets:–
- The stock of consumables or raw materials held for use in business or profession.
- Personal belongings meant for personal use like clothes, furniture, etc.
- A piece of agricultural land is located in a rural area.
- Special bearer bonds, 6.5% gold bonds (1977), 7% gold bonds (1980), or national defense gold bonds (1980) which the Central Government has issued.
- Gold deposit bond (1999), issued under the gold deposit scheme or deposit certificate issued under the Gold Monetisation Scheme, 2015, notified by the Central Government.
What are the Different Types of Capital Assets?
Capital assets are divided into two types based on the period after which they are sold. The types of capital assets are as follows –
- Short-term Capital Assets
- Long-term Capital Assets
What are Short-term Capital Assets?
Short-term capital assets are those held for less than or equal to 36 months. This means that if you sell off the asset within 36 months of buying it, it would be called a short-term capital asset. However, in some cases, the holding period is reduced to 24 months and 12 months. These cases include the following –
- If the asset is an immovable property like land, building, or house, then the holding period would be considered 24 months. This means that if you sell off an immovable property within 24 months of buying it, it would be called a short-term capital asset.
- Similarly, equity shares of a company listed on the Recognized stock exchange, securities listed on the Recognized stock exchange, UTI units, equity-oriented mutual fund units, and zero-coupon bonds have a holding period of 12 months. If these assets are sold off before 12 months of purchase, they would be called short-term capital assets.
What are Long-term Capital Assets?
Long-term capital assets are those held for more than 36 months and then sold off. Immovable property sold after 24 months would be categorized as a long-term capital asset. In the case of equity shares, securities, mutual fund units, etc., however, the holding period of 12 months is applicable. If sold off after 12 months, they would be called long-term capital assets.
Generally, the holding period of capital assets to be considered as long-term is 36 months. However, there are certain exceptions to this rule. Here’s a summary of different types of capital assets and the period of holding, after which they are considered long-term capital assets -
| Capital Assets | Holding Period |
|---|---|
| Equity Shares or Preference Shares in a company (listed) | 12 months |
| Equity Shares or Preference Shares in a company (unlisted) | 24 months |
| Immovable Property (land or building or both) | 24 months |
| Securities like bonds, debentures, derivatives, and government securities (listed) | 12 months |
| Units of UTI (Unit Trust of India) (listed or unlisted) | 12 months |
| Units of equity-oriented mutual funds (listed or unlisted) | 12 months |
| Units of debt-oriented mutual funds (listed or unlisted) | 36 months |
| Zero coupon bonds (listed or unlisted) | 12 months |
How are Inherited Capital Assets Classified?
When acquiring an asset through gift, will, succession, or inheritance, the duration for which the previous owner held the asset is considered.
- For bonus shares or rights shares, the holding period starts from the date of allotment of bonus shares.
- This consideration applies to determining whether the asset qualifies as short-term or long-term capital asset.
What are the Different Types of Capital Gain Tax?
Now that you have understood what capital assets are and their types, it’s time to understand the types of capital gains. Capital gains are divided into short-term capital gains and long-term capital gains –
Short-Term Capital Gain Tax
Short-term capital gains (STCG) are the profits you earn when you sell off your capital assets within one year of holding them. Note that the holding period varies as per the capital asset.
- When the security transaction tax is applicable: Short-term capital gain tax is 15%
- When a security transaction tax is not applicable, the short-term capital gain tax will be calculated based on the taxpayers' income and will be automatically added to the taxpayer's ITR and charged at normal slab rates.
Long-Term Capital Gain Tax
Long-term capital gain tax (LTCG) are the profits you earn when you sell off your capital assets after one year. Note that the period of holding for different assets to be claimed as long-term assets varies according to the asset.
- Long-term capital gain tax is applicable at 20% except on the sale of equity shares and the units of equity-oriented funds.
- Long-term capital gains are 10% over and above Rs 1 lakh on the sales of equity shares and units of equity-oriented funds.
Are you ready to simplify your capital gain tax filing process and maximize your returns? At Tax2win, we specialize in providing expert assistance tailored to your unique financial situation. Our comprehensive services ensure accuracy, compliance, and peace of mind for our clients. Hire an online CA..
How to Calculate Capital Gains Tax?
Short-term capital gains Calculations
| Full value of consideration | xxxxx |
| (-) Expenses incurred on transferring the asset | (xxxx) |
| (-) Cost of acquisition | (xxxx) |
| (-) Cost of the improvement | (xxxx) |
| Short-term capital gains | xxxxx |
Let’s understand it with an example. A house property was bought on 1st January 2021 for INR 50 lakhs. On 1st January 2022, INR 5 lakhs were spent on improving the house. On 1st November 2022, the house was sold for INR 65 lakhs.
Since the house was sold after 22 months of buying it, it would be categorized as a short-term capital asset. The gain from selling the house would be called a short-term capital gain, and it would be calculated as follows –
| The full value of consideration | INR 65 lakhs |
| (-) Cost of acquisition | INR 50 lakhs |
| (-) Cost of improvement | INR 5 lakhs |
| Short-term capital gains | INR 10 lakhs |
Long-Term Capital Gain Calculations
| Full value of consideration | xxxxx |
| (-) Expenses incurred in transferring the asset | (xxxx) |
| (-) Indexed cost of acquisition | (xxxx) |
| (-) Indexed cost of the improvement | (xxxx) |
| (-) expenses allowed to be deducted from the full value of the consideration | (xxxx) |
| (-) exemptions available under Sections 54, 54EC, 54B and 54F, etc. | (xxxx) |
| Long-term capital gains | xxxxx |
Let’s understand this with the help of an example -
A house property was purchased on 1st January 2000 for INR 20 lakhs. On 1st January 2005, repairs were done on the house, which amounted to INR 5 lakhs. On 1st January 2023, the house was sold for INR 75 lakhs. A brokerage was paid to the broker, which was INR 1 lakh. What would be the capital gain amount?
Solution:
Since the asset has been held for more than 36 months, it is a long-term capital asset, and the gain is a long-term capital gain. The gain would be calculated as follows –
| Particulars | Calculation | Amount |
|---|---|---|
| The full value of consideration | - | INR 75,00,000 |
| Less: indexed cost of acquisition | Cost of acquisition * CII of the year in which the asset is sold / CII of the year in which the asset was acquired = 20 lakhs * (CII of 2022-23 / CII of 2001-02 since it is the base year)= 20 lakhs * (331/100) | INR 66,20,000 |
| Less: indexed cost of improvement | Cost of improvement * CII of the year in which the asset is sold / CII of the year in which the asset was improved = 5 lakhs * (CII of 2022-23 / CII of 2004-05)= 5 lakhs * (272/113) | INR 14,64,602 |
| Less: brokerage paid | - | INR 1,00,000 |
| Long term capital gain or Long term capital Loss | - | INR -6,84,602 |
What is Indexation?
Indexation of costs is done to factor in the inflation over the years when you hold the capital asset. Since inflation decreases the value of money, indexation of the acquisition and improvement costs increases the amount of these costs, thereby lowering the capital gain earned. To calculate indexation, Cost Inflation Index (CII) accounts for the inflation incurred over the holding period. To calculate the indexed costs, the following formula is used –
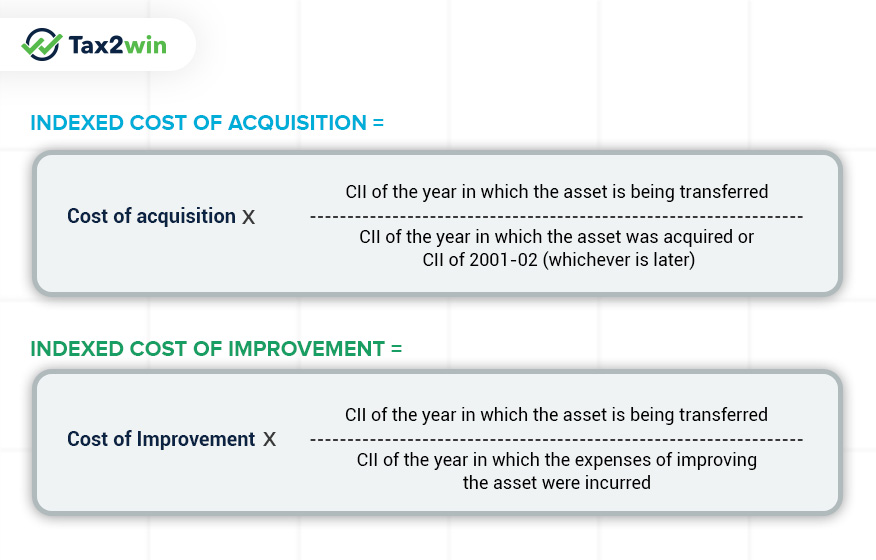
The base year for CII has changed from 1981 to 2001. That is why, when calculating the indexed cost of acquisition, CII of 2001-02 is considered if the asset was purchased before the financial year 2001-02.
With the shift in the base year, the CII numbers have also changed. The CII for different years, as determined by the Central Government, are as follows –
| Financial year | Cost Inflation Index (CII) |
|---|---|
| 2001-02 | 100 |
| 2002-03 | 105 |
| 2003-04 | 109 |
| 2004-05 | 113 |
| 2005-06 | 117 |
| 2006-07 | 122 |
| 2007-08 | 129 |
| 2008-09 | 137 |
| 2009-10 | 148 |
| 2010-11 | 167 |
| 2011-12 | 184 |
| 2012-13 | 200 |
| 2013-14 | 220 |
| 2014-15 | 240 |
| 2015-16 | 254 |
| 2016-17 | 264 |
| 2017-18 | 272 |
| 2018-19 | 280 |
| 2019-20 | 289 |
| 2020-2021 | 301 |
| 2021-2022 | 317 |
| 2022-2023 | 331 |
| 2023 - 2024 | 348 |
Note: Getting help from tax experts can make capital gains tax calculation extremely easy and quick. All you have to do is hire an online CA and give them a summary of your capital gain transactions during the year. These experts will not only calculate your capital gains tax but also file your ITR accurately on time.
What is Surcharge?
Income tax surcharge is the additional tax charged on the income tax payable. It is levied on the taxpayers having a higher income inflow during the year. Given below are the surcharge rates on STCG and LTCG for individuals, HUF, AOP, BOI, and AJP -
| Nature of Income | Range of Total Income | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Up to Rs. 50 lakhs | More than Rs. 50 lakhs but up to Rs. 1 crore | More than Rs. 1 crore but up to Rs. 2 crores | More than Rs. 2 crores but up to Rs. 5 crores | More than Rs. 5 crores | |
| Short-term capital gain covered under Section 111A/115AD | Nil | 10% | 15% | 15% | 15% |
| Long-term capital gain covered under Section 112A/115AD | Nil | 10% | 15% | 15% | 15% |
What are the Expenses Allowed for Capital Gains?
These are the expenses that were necessary to be incurred when selling the asset. Without these expenses, the asset would not have been purchased. These expenses, since mandatory, are allowed to be deducted from the full value of the consideration, which lowers the selling price / increases the cost of acquisition, and also decreases the capital gain. The expenses allowed to be deducted include the following –
Expenses Allowed for Property, Shares and Jewelry
| House Property | Shares | Jewelry |
| . Stamp paper cost . Brokerage or commission paid to a broker for arranging a buyer . Traveling expenses incurred for the sale of the asset . Expenses incurred in obtaining succession certificates, paying the executor of the Will, and other legal procedures if the property is acquired through a Will or inheritance |
Commission paid to the broker for selling the shares. | Commission paid to the broker for arranging a buyer for the jewelry |
Capital Gains Tax Rates
Given below is the summary of the holding period and the capital gains tax rates for different capital assets -
| Capital Asset | Holding Period for Long Term Capital Asset | Long Term Capital Gain Tax (LTCG) | Short Term Capital Gain Tax (STCG) | Remarks |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stocks | > 12 months | 10% of gain | 15% of gain | LTCG applicable if total exceeds Rs. 1 Lakh in a financial year. |
| Unit Linked Insurance Plan (ULIPs) | > 12 months | 10% of gain | 15% of gain | LTCG applicable if total exceeds Rs. 1 Lakh in a financial year. |
| Equity Oriented Mutual Funds | > 12 months | 10% of gain | 15% of gain | LTCG applicable if total exceeds Rs. 1 Lakh in a financial year. |
| Other Mutual Funds | > 36 months | 20% with inflation indexation | Taxed based on income tax slab | |
| Government and Corporate Bonds | > 36 months | 20% with inflation indexation | Taxed based on income tax slab | |
| Gold | > 36 months | 20% with inflation indexation | Taxed based on income tax slab | |
| Gold ETF | > 12 months | 10% of gain | Taxed based on income tax slab | LTCG applicable if total exceeds Rs. 1 Lakh in a financial year. |
| Immovable Property | > 24 months | 20% with inflation indexation | Taxed based on income tax slab | |
| Movable Property | > 36 months | 20% with inflation indexation | Taxed based on income tax slab | No tax for LTCG reinvested in approved assets. |
| Privately held Stocks | > 24 months | 20% with inflation indexation | Taxed based on income tax slab |
Note: Taxes mentioned do not include any surcharge levied on income tax.
Tax Exemption on Capital Gain
Because capital gains tax tends to erode a significant portion of earnings, it becomes critical for individuals to utilize tax-saving strategies to help them reduce their tax liability. To assist individuals in minimizing their capital gains tax liability, the government provides a list of exemptions under capital gains. These tax exemptions are known as capital gains exemptions.
Exemption Under Section 54: Sale of House Property on Purchase of Another House Property
The exemption on two house properties shall be available once in a lifetime to a taxpayer, provided the capital gains do not exceed Rs. 2 crores. The taxpayer is only required to invest the number of capital gains, not the complete sale proceeds. The exemption will be limited to the total capital gain on sale if the purchase price of the new property is higher than the number of capital gains.
The following conditions must be met to enjoy the benefit:
- The new property can be purchased either one year before or two years after the previous property has been sold.
- Gains can also be invested in property construction, but construction must be completed within three years of the sale date.
- In the 2014-15 Budget, it was made clear that only one house property could be purchased or built with capital gains to qualify for this exemption.
- Please remember that this exemption can be revoked if the new property is sold within three years of its purchase or completion of construction.
Exemption Under 54B: Transfer of Land Used for Agricultural Purposes
An exemption is available under Section 54B when you make short-term or long-term capital gains from the transfer of land used for agricultural purposes – by an individual, the individual's parents, or a Hindu Undivided Family (HUF) – for two years before the sale. The lesser of the capital gain on the sale of agricultural land or the investment in new assets is exempt from tax. You must reinvest in new agricultural land within two years of the transfer date.
- The new agricultural land purchased to claim capital gains exemption should not be sold within three years of its purchase date.
- If you cannot purchase agricultural land before the due date for filing your income tax return, the number of capital gains must be deposited in any branch (except rural branches) of a public sector bank or IDBI Bank before the due date.
- Exemptions can be claimed for the amount deposited. If the amount deposited under the Capital Gains Account Scheme was not used to purchase agricultural land, it should be treated as capital gains of the year in which the period of two years from the date of sale of land elapsed.
Exemption Under Sections 54 E, 54EA, and 54EB – Profits from Investments in Certain Securities
This capital gains exemption applies to capital gains derived from the transfer of long-term capital assets. Individuals can take advantage of such long-term capital gain exemptions if they reinvest in securities such as targeted debentures, UTI units, government securities, government bonds, etc.
The following conditions must be met–
- Individuals must reinvest in such new securities within six months of the transfer of capital assets.
- If the individual plans to sell the new securities before 3 years or 36 months, the previously offered exemption would be deducted from the total cost to determine the capital gains.
It is important to note that any loan availed against these securities before 3 years would be treated as a capital gain.
Exemption Under Section 54EC – Profits from the Sale of a Long-term Capital Asset are Exempt from Tax if Reinvested in Specific Long-term Assets.
Long-term capital gains on the sale of long-term assets would be qualified for long-term capital gain exemption. Individuals will be eligible for such exemptions if they reinvest their proceeds in assets of either the Rural Electrification Corporation or the NHAI.
Such capital exemptions are available if and only if the following conditions are met:
- Individuals reinvest the proceeds into specified assets within six months of the asset's sale.
- Capital gains should not exceed the amount invested. If only a portion of the gains were reinvested, the capital gain exemption would apply only to the reinvested amount.
- Specific assets must be held for a minimum of 36 months.
Exemption Under Section 54EE – Profits from a Transfer of Investments.
Capital gains derived from the transfer of long-term capital assets would be eligible for a capital gain exemption if –
- Individuals should reinvest their proceeds within six months of receiving them.
- If individuals sell their new securities before 36 months, the previously offered exemption is subtracted from the cost to calculate capital gains.
- If a loan is taken out against new securities before 36 months, the capital gains are taxed.
- In the current and following fiscal years, such investments should not exceed Rs. 50 lakh.
Exemption Under Section 54F: Capital Gains on the Sale of Any Asset Other Than a Home.
Exemption under Section 54F is available when capital gains are realized from the sale of a long-term asset other than a home. To qualify for this exemption, you must invest the entire sale consideration, not just the capital gain, in purchasing a new residential house property. Purchase the new property either one year before or two years after the previous one. You can also use the profits to fund the construction of a home. The construction, however, must be completed within three years of the date of sale.
In Budget 2014-15, it was stated that only one house property could be purchased or built from the sale consideration to claim this exemption. This exemption can be revoked if the new property is sold within three years of purchase. If you meet the conditions mentioned and invest the sale proceeds in the new house, the entire capital gain will be tax-free.
However, if you invest a portion of the sale proceeds, the capital gains exemption will be calculated as follows: capital gains x cost of new house /net consideration = capital gains x cost of new house /net consideration.
Under Capital Gains, any profit that is made from a capital asset transfer during the year is taxable. Let us help you navigate the complexities of capital gains taxation and optimize your returns. Hire a tax expert and file your taxes.
Amendment to Section 54 - Capital Gain Exemption
Investing in property has long been a favored strategy for individuals seeking secure and potentially profitable investments. The approach of buying property, holding it for a few years, and selling it at a higher price has been embraced by many as a reliable investment mantra.
In many cases, the owners of residential properties need to sell their houses due to reasons like moving to a new city, switching jobs, retirement, etc. Under Section 54 of the Income Tax Act, if the seller of a residential property acquires or constructs another residential property from that amount, he or she gets benefits from capital gains tax. In this case, the objective is not to earn income from selling the old house but to acquire another suitable house. In other words, when an assessee sells a residential property and purchases or constructs another residential house property, he or she gets an exemption from capital gains under Section 54 of the Income Tax Act.
Revised Section 54 – For individuals or Hindu Undivided Families (HUFs) selling a residential house property (Long Term Capital Asset), the exemption on capital gains will be limited to Rs. 10 crore. Even if the new house purchased exceeds this limit, the maximum exemption allowed will be capped at Rs. 10 crore. For instance, if the capital gain is Rs. 18 crore and the individual buys a new house worth Rs. 18 crore, the exemption will be restricted to Rs. 10 crore.
Revised Section 54F – Similarly, for individuals or HUFs selling a capital asset other than residential property (Long Term Capital Asset), the maximum exemption on capital gains will also be limited to Rs. 10 crore. Any investment exceeding this limit will not be considered for exemption. A provision is added to exclude the portion of net consideration exceeding Rs. 10 crore from the calculation of exemption under this section. For example, if the consideration from selling a plot is Rs. 15 crore, with a capital gain of Rs. 8 crore, and the individual invests Rs. 12 crore in a new residential house, the exempted gain will be calculated as Rs. 8 * 10/15 = Rs. 5.33 crore, and the taxable amount will be Rs. 8 - 5.33 crore = Rs. 2.67 crore.
These amendments also apply to the provisions related to Capital Gains Accounts Scheme (CGAS), ensuring that the maximum exemption allowed is restricted to Rs. 10 crore. These changes aim to streamline and regulate the exemption provisions under the capital gains head.
ITR Filing for Capital Gains
If you have any capital gains in the previous year, you must mandatorily file ITR. Capital gains/losses during the year have to be reported in ITR-2 and ITR-3. You can also claim the available exemptions while filing your ITR.
However, filing ITR for capital gains can be complicated. Don’t worry! Our tax experts can help you file your ITR while ensuring that you don’t miss out on any potential deductions. If you are looking to save income tax on capital gains, book an online CA Now.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q- Do I have to pay capital gains tax if my total income is less than 2.5 Lakh?
If the total income of the assessee including capital gains, is below the basic exemption limit, then no tax is levied.
Q- What are the best ways to avoid capital gain tax?
There are various ways to avoid capital gains tax by investing the amount of gain in the investment schemes of the government and other methods specified by CBDT
Q- Is advance tax paid on Capital Gain & Casual Income? If yes, then how would the amount be calculated?
Advance tax should be paid on capital gain income and casual incomes. The amount is calculated by adding the capital gain with the total income, and tax is calculated.
Q- What is the capital gains tax rate for listed, and unlisted bonds, and debentures in India for FY 22-23 (AY 23-24)?
If the capital gains are short-term, then the rate for both listed and unlisted bonds and debentures are as per slab rates, and if gains are long-term, then the rate for listed bonds is 10% and for unlisted 20%
Q- Why does selling machinery attract short-term capital gains tax and not a long-term capital gain tax?
Capital assets on which depreciation is charged are sold to attract short-term capital gain. The cost of acquisition is taken in this case as the WDV of the assets.
Q- Do I have to pay short-term capital gains tax if I am in the 5% ordinary income tax bracket?
Short-term capital gains are taxed at the slab rates of the assessee. So assessees must pay the tax on short-term capital gain at its tax brackets.
Q- Are profits generated by high-frequency trading algorithms taxed as capital gain or income?
It depends on the nature of the assessee's business. If the trading of shares is the assessee's business, then it will be taxed under business income and otherwise under capital gain.
Q- Can you avoid capital gains taxes if you move to another country?
No, it cannot be avoided. The tax on capital gain must be paid irrespective of the person's residential status.
Q- Are cryptocurrency capital gains taxable in India?
Yes, cryptocurrency gains are considered income under Business Income in India. You'll pay a flat 30% tax on any net cryptocurrency gains (total sales proceeds minus cost basis and expenses.
Q- Do I need to report cryptocurrency transactions on my tax return in India?
Yes, you must report all cryptocurrency transactions, including gains, losses, and exchange activity, on your tax return.
Q- Do I need to pay capital gains tax on inherited assets in India?
In India, you don't pay capital gains tax on inherited assets if you sell them immediately. Your cost basis for the asset becomes the fair market value at the time of inheritance, eliminating any initial capital gain (or loss).
Q- What if I hold onto an inherited asset for some time before selling it in India?
If you hold onto the asset beyond a year, the cost basis becomes the fair market value at the time of inheritance plus any indexation benefits to account for inflation. You'll pay capital gains tax on any increase in value after adjusting for indexation.
Q- Are capital gains on ESOPs taxable in India?
The tax treatment of ESOPs in India depends on how they are exercised and sold. You may pay ordinary income tax at the applicable slab rate on the difference between the exercise price and the fair market value at the time of exercise. Any further appreciation when you sell the shares is taxed as long-term capital gains at 10% (exceeding Rs. 1 lakh) or 20%.
People also ask
- Types Of Income, Deductions, Tax Slabs & e-Filing ITR Online
- Advance Tax: Calculate & Make Payment Online
- URN Status - How to check your URN Status?
- Udyog Aadhar Registration
- Self Assessment Tax
- Securities Transaction Tax (STT)
- Section 92E - Furnishing Reports For International Transactions
- Presumptive Income Taxation Under Income Tax Act
- Section 44ADA - Presumptive Taxation
- Section 44AD - Presumptive Taxation
- Section 12A - Tax Exemptions for Charitable Trusts & NGOs
- PRAN Card - Permanent Retirement Account Number Guide
- Minimum Alternative Tax - Applicability & Calculation of MAT Credit
- Section 56 - Taxation of Wedding/Marriage Gifts Received
- Income Tax on Dividends - How dividends are taxed?
- Income Tax on Awards & Prizes - Lottery, Game Shows, Puzzle
- Claim Tax Credit on Foreign Income of a Resident Indian
- Income Tax Audit Under Section 44AB of Income Tax Act
- Income Tax Act & Laws - 1961 & 1962
- Gross Total Income - Computation of Total Taxable Income
- Form 10E - Claim Income Tax Relief under Section 89(1)
- Dividend Mutual Funds
- Cost Inflation Index (CII)
- Agricultural Income - Types & Tax Calculation
- 5-Year Post Office Recurring Deposit
- Voter ID /Election Card - Documents, Application, Eligibility
- Total Income - How to Calculate It?
- Income Tax India E - filing Login
- KYC (Know Your Customer) - How to Check Your KYC Status
- Section 87A - Tax Rebate under Section 87A
- Union Budget 2019 - Key Highlights
- Income Tax Form 60
- Income Tax For Self Employed Business, Profession & Freelancers
- Govt. Jobs v/s Private Jobs - Comparative study on benefits
- Section 234F - Penalty for Late Filing of Income Tax Return
- Section 234C - Interest on Deferred Payment of Advance Tax
- Section 234B - Interest on Delayed Payment of Advance Tax
- Section 234A - Interest Penalty on Delayed ITR Filing
- Section 234F - Penalty for Late Filing of Income Tax Return
 Trusted by 2 Million+ Users
Trusted by 2 Million+ Users 4.8 Star User Rating
4.8 Star User Rating Secure & Safe
Secure & Safe







